What is 3D Printing?
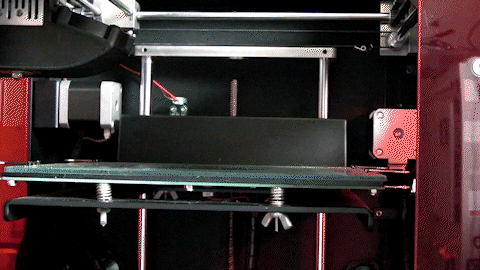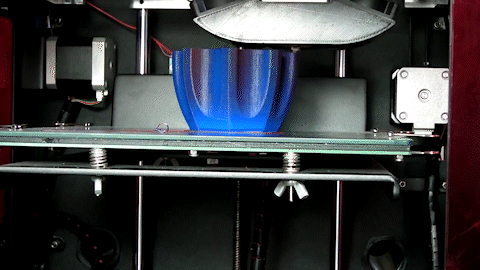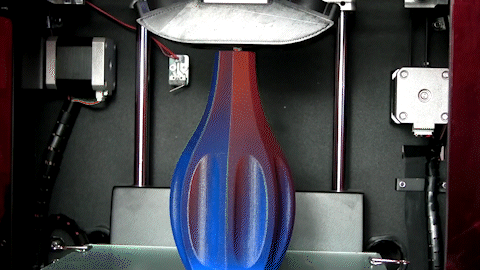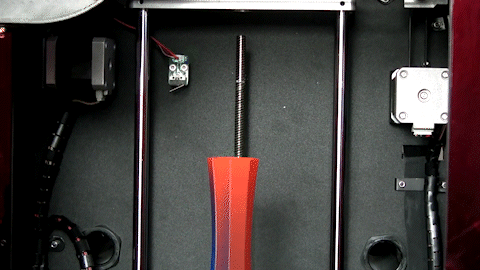
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by building layers of material on top of each other. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that involve removing material from a block to create a part, 3D printing starts with a digital 3D model that is sliced into thin layers, and then the printer adds material layer-by-layer until the final object is created.
The material used in 3D printing can vary depending on the type of printer and the intended application, but common materials include plastic, metal, resin, and ceramics. 3D printing is used in a wide variety of industries including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer products, among others. It can be used to create prototypes, custom products, replacement parts, and even complex organic shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
The material used in 3D printing can vary depending on the type of printer and the intended application, but common materials include plastic, metal, resin, and ceramics. 3D printing is used in a wide variety of industries including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer products, among others. It can be used to create prototypes, custom products, replacement parts, and even complex organic shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.

Leave a comment